Interview
The state of Maple Finance
Token Terminal
•
In this series, we break down the business of a crypto project and learn about the drivers behind the data you see on Token Terminal's charts.
Watch the full interview on YouTube, listen to the audio version on any podcast platform, or read the write-up below.
Below is a write-up of our discussion about the current state of Maple Finance with Co-Founder Joe Flanagan (edited for clarity).
This interview was recorded on March 24th. Some information has been updated to reflect the current state of Maple Finance.
Q: Could you give a quick intro to Maple Finance for those not yet familiar?
Maple finance is an institutional capital market currently built on Ethereum and Solana. Maple enables institutional borrowers to borrow from the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem. The way the protocol works is that lenders supply capital into pools, and this capital is lent out to institutional borrowers. Maple's unique feature is that each pool is managed by a role we call the pool delegate. Pool delegates are responsible for negotiating terms, underwriting, and conducting due diligence on institutional borrowers – enabling undercollateralized lending to happen.
Overcollateralized lending protocols like Aave and Compound have dominated the DeFi ecosystem since the summer of 2020. With Maple, we're enabling true credit creation so companies are able to borrow undercollateralized and source funding in a more capital-efficient way to continue growing their businesses. To date, we've had great adoption with this model focusing on crypto native market makers who have been able to continue growing their businesses with the supply of capital from Maple. As we continue to expand, we'll also explore other borrower verticals. It’s important to keep in mind that we are not lending capital ourselves, but rather providing a capital market infrastructure that enables these capital flows and borrowing to occur. We see this as being something that can scale from where we are today into the tens of billions in the future.
Q: Can you walk us through Maple's business model and how you're generating cash flow at the moment?
There are two main revenue streams that exist on the Maple protocol. For the Maple treasury, the main source of income is establishment fees that are paid when a borrower sources capital and takes out a loan. The establishment fee is currently set at one percent, of which two-thirds go to the Maple treasury (protocol revenue). The remaining one-third goes to the pool delegate; the person responsible for underwriting and agreeing on terms with the borrower (supply-side revenue).
In terms of other revenue generated on the platform, we have the ongoing fee which is a portion of the interest that is provided to both the pool delegate for their role in underwriting, and to a separate role and function that is called cover. Cover providers are able to post Maple tokens in combination with USDC to a cover reserve that protects lending capital. In the event of default, these cover providers would be liquidated first – protecting the lenders that sit above them. In more detail, the ongoing fee is a portion of the interest revenue generated by the pool of which typically 10% goes to the pool delegate, 10% to the cover reserve, and the remaining 80% to the lenders that are providing capital to the borrowers (supply-side revenue).
To date, we've been able to issue over a billion dollars in loan originations and have active liquidity of around 825 million dollars. There are significant interest revenues coming to the protocol, of which the majority goes to the lenders that supply the capital to the marketplace.
Q: Looking at the chart below, we can see that your revenues are spread out quite a bit. Could you explain why that is?
The reason it looks a little bit lumpy is a result of two functions. Firstly, loan establishment fees are generated when a loan is taken out. You'll see that e.g. over the Christmas period there's a real lull because no loans were originating as everyone was on holiday. Sometimes a big loan will be taken out bringing in a big influx of cash flow into the Maple treasury, versus other days where there would be none. Secondly, ongoing fees are distributed to lenders according to the agreed loan repayment schedule. If we were to streamline this across a period of time, you would see that the protocol revenues have been increasing dramatically. This is a function of the amount of active liquidity in the platform and the number of loan originations that are happening.
Q: Looking at the lending market in general, revenue's have been in a downtrend for the past months as per below. Can you walk me through the current drivers behind Maple's growth, and what you are doing differently, as you're growing against the market trend?
The biggest thing for us is continuing to source new liquidity and new lending capital, which will then enable us to originate more loans. We have the benefit of liquidity and capital cycling that's already in the protocol, and bringing in new lender capital is super important for the continuation of our growth. What we've seen over the last few months is a bit of a flattening over the Christmas period when no new lending capital was coming in, so the net between new lending capital and withdrawals was around zero, after which we've continued to be able to ramp that up. Over the last two to three months, we've seen a real broader adoption of Maple and an understanding that we are an institutional capital market that's providing a differentiated offering.
A lot of yield-generating products that exist in DeFi are really only inflationary token models where you're not able to have underlying real cash flows coming in from companies. Maple provides people the ability to lend into a pool, provide capital to a real business that's generating real cash flows, and then earn part of those cash flows. Our main differentiator is that we're providing true credit creation and actual cash flows from real businesses. Enabling people in DeFi to access this potentially for the first time is really exciting.
Q: As you're tapping into the undercollateralized lending market, could you explain how the loan approval process works?
The way it works is that all potential borrowers on the Maple platform go through a KYC and AML process performed by us in order to become approved borrowers. Once you're an approved borrower, you're able to access the various pools that exist, and interact with pool delegates that are on the platform. The pool delegates control the interaction with borrowers, and whilst they are never in custody of the funds, they are in charge of negotiating the terms and determining whether a borrower is worthy to originate a loan from their pool. This process is really our only bottleneck to the growth of the platform.
In more detail, pool delegates perform the credit due diligence and ensure only the best and most reputable borrowers come to the platform. Fortunately, we're able to have many pool delegates across many borrower verticals which will enable real scalable growth.
As mentioned before, Maple is an infrastructure and a platform – not necessarily a lender. We really see ourselves as a technology company that will facilitate an entire ecosystem and marketplace for borrowers to access all of their capital needs and lenders to access many different yield opportunities.
Q: How do you see the composition of the borrowing volume developing in the future
This is an interesting one, because to date we've been solely focused on crypto native market makers, which have been a great source of risk-return for lenders in the Maple protocol. The borrowers that we enable on the platform are delta neutral, so they're not taking any market risk or any “price of bitcoin” -risk. They're only taking on arbing spreads, which has been lucrative for us and a great catalyst for growth in being the right risk dynamic to enter the market and build a platform from scratch. As we look to the future, we want to break out into other borrower verticals. Our next priority from a borrower vertical perspective is crypto miners. We’re looking to launch a crypto mining pool within the next quarter and expand that offering to a broader subset of crypto miners. We've seen a real development in that ecosystem where much more of the hash rate is moving back to North America, and we think there's a real opportunity for us.
In the longer term, we see ourselves developing into being not necessarily just crypto native borrowers. There's the potential for SaaS and FinTech companies to come to the platform and access capital. When you really think about it, DeFi and TradFi are very segmented. Our thinking is that in five years’ time that will just become finance again, and Maple will be a real instigator for that transition and for TradFi participants to both access capital as borrowers and lend capital through the Maple platform.
Q: How do you choose the pool delegates and how is counterparty risk managed on Maple?
When we launched we started with only two pool delegates (Orthogonal Trading and Maven). Since then we've onboarded Block Tower, which is a reputable hedge fund in the space with real credit expertise, but they're currently only using the platform to provide their own capital and will shortly be enabling external capital to be provided into the pool.
We started with two permissionless pools in which anyone could participate as a lender, and the pools that we've launched subsequent to that have been majority focused on permissioned pools. This really plays into the institutional theme where KYC and AML processes are really important to a lot of institutions. We only allow whitelisted, KYC'd and AML'd participants into some of our permissioned pools. For example, the Alameda pool that you see on the platform is a single borrower pool that only Alameda is accessing capital from, and only KYC’d and AML’d accredited investors are providing capital. More recently we saw the launch of the Celcius pool. Celcius is only providing their lending capital into the pool to use Maple as infrastructure and a service to manage their own loan book on our platform.
Q: What is the average loan duration on Maple?
When we launched we started with 90 days. Now, the average borrower that has built up a reputation on the platform has been borrowing for an average 180-day term.
Q: What is the average loan turnover rate? So from a capital-efficiency perspective, how many times can you take an establishment fee from the same liquidity?
As our average loan duration is towards the back end of 180-days, we are able to turn our capital twice a year. But the important thing to remember – and this is an update we made more recently on the establishment fee – is that it's an annualized rate. We don't make the borrower pay an establishment fee that's fixed at the portion of the loan that they're taking out every time they take out a loan – it's annualized based on the term of their loan. This means that whether a borrower takes out a loan for a year or for one month, Maple is effectively earning the same amount.
Q: Is there anything else on the future of Maple that you'd like to share that we didn't discuss yet?
We touched on all of the new borrower verticals that we can potentially expand into and I think everyone hopefully has a good context for us being a capital marketplace and infrastructure that will enable broad adoption of institutional lending using DeFi technology.
The only thing I would add is that we've got some exciting updates coming to our tokenomics with the introduction of xMPL. We will be adding a lot of incentives and use cases for being a Maple token holder as well as other opportunities for people that participate in the ecosystem and marketplace that we're building.
xMPL staking is now live: Maple will use 50% of protocol revenues to buy MPL back from the open market. This MPL will then be evenly distributed to participants that stake their MPL into a Maple owned smart contract and participate in the protocol long-term.
The interview concluded.
Make sure to check out Maple Finance on Token Terminal and subscribe to our YouTube channel so you don’t miss any episodes.
The authors of this content, or members, affiliates, or stakeholders of Token Terminal may be participating or are invested in protocols or tokens mentioned herein. The foregoing statement acts as a disclosure of potential conflicts of interest and is not a recommendation to purchase or invest in any token or participate in any protocol. Token Terminal does not recommend any particular course of action in relation to any token or protocol. The content herein is meant purely for educational and informational purposes only, and should not be relied upon as financial, investment, legal, tax or any other professional or other advice. None of the content and information herein is presented to induce or to attempt to induce any reader or other person to buy, sell or hold any token or participate in any protocol or enter into, or offer to enter into, any agreement for or with a view to buying or selling any token or participating in any protocol. Statements made herein (including statements of opinion, if any) are wholly generic and not tailored to take into account the personal needs and unique circumstances of any reader or any other person. Readers are strongly urged to exercise caution and have regard to their own personal needs and circumstances before making any decision to buy or sell any token or participate in any protocol. Observations and views expressed herein may be changed by Token Terminal at any time without notice. Token Terminal accepts no liability whatsoever for any losses or liabilities arising from the use of or reliance on any of this content.
Stay in the loop
Join our mailing list to get the latest insights!
Continue reading

Customer stories: Token Terminal’s Data Partnership with Linea
Through its partnership with Token Terminal, Linea turns transparency into a competitive advantage and continues to build trust with its growing community.
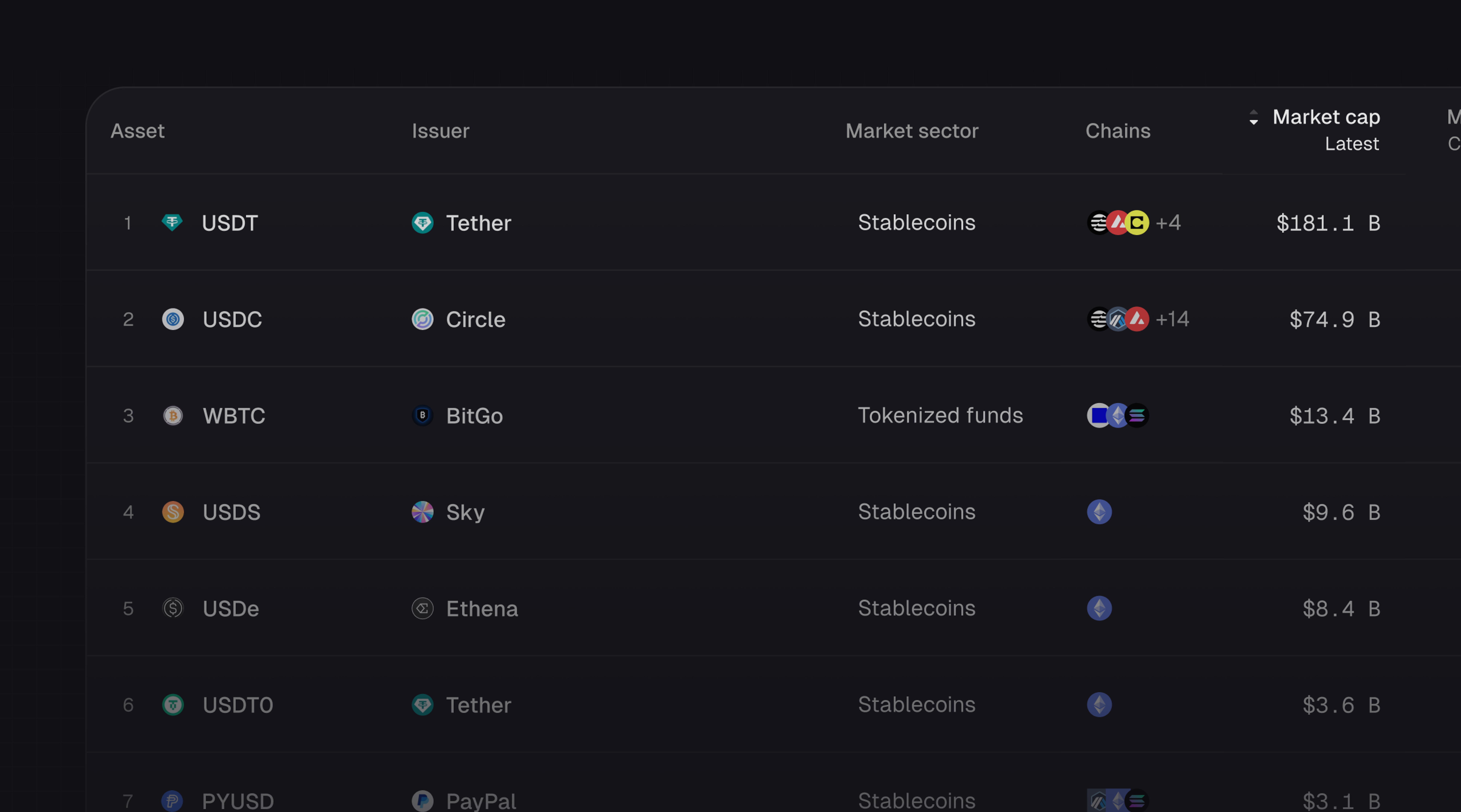
Introducing Tokenized Assets
Token Terminal is expanding its standardized onchain analytics to cover the rapidly growing category of tokenized real-world assets (RWAs) – starting with stablecoins, tokenized funds, and tokenized stocks.

Customer stories: Token Terminal’s Data Partnership with EigenCloud
Through its partnership with Token Terminal, EigenCloud turns transparency into a competitive advantage and continues to build trust with its growing community.