Research
Research series
Token Terminal
•
This is the sixth post in our research series. In this series, we publish data-driven analysis on specific blockchains, dapps, and market segments. Let’s dig in!
Topic: Cosmos, a blockchain (Hub) and a new standard for blockchain interoperability (IBC).
Cosmos is a network of blockchains that can securely communicate between each other to transfer data and value. Instead of having decentralized applications (dapps) compete for the resources of a single blockchain, such as Ethereum, the team behind Cosmos envisions a scalable network of application-specific blockchains. The network’s first blockchain, Cosmos Hub, was launched in 2019 and several well-known projects have since been launched on the network.
In this article, we will provide an overview of the project and look at its historical performance using Token Terminal’s data.
Overview
To get an understanding of Cosmos, let’s first look at Ethereum. On Ethereum, all dapps are deployed on the same blockchain. While this allows dapps to benefit from Ethereum’s security, it also fundamentally limits their scalability. Since all dapps compete for the limited resources of a single blockchain, they are limited by the number of transactions the blockchain can process over a given period of time. This can lead to a poor user experience by making the transaction fees (i.e., gas price) very high. Additionally, the design choices and governance decisions of Ethereum impose limitations on the functionality that the dapps can implement.
Cosmos aims to solve the aforementioned issues by building a decentralized network of application-specific blockchains. The whole ecosystem, i.e., the network of blockchains, is known as the Cosmos network. Application-specific blockchains are blockchains that are customized to optimally run a single application. In a previous entry of the Token Terminal Research Series, we discussed the Centrifuge Chain, which is an application-specific blockchain, although on Polkadot.
Cosmos’ goal is to provide the fundamental building blocks and open-source software tools to enable developers to efficiently create secure and efficient application-specific blockchains.
In order to understand the Cosmos software stack, it is helpful to think about blockchains using three conceptual layers. First, the application layer processes transactions. Second, the networking layer transfers data between the nodes. Third, the consensus layer allows the nodes to agree on the current state of the system. With Cosmos’ Tendermint, developers can create the networking and consensus layers of the blockchain that can support thousands of transactions per second. Cosmos Software Development Kit (SDK) is a framework for building the application layer of the blockchain.
The backbone of the Cosmos ecosystem is the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol. It enables the ecosystem’s blockchains to communicate between each other to securely transfer data and value.
At the network level, Cosmos’ blockchains are divided into Zones and Hubs. Zones are application-specific blockchains and hubs are designed to connect the zones together. This is required to avoid the number of connections from growing too high, because the number of possible links in a network grows quadratically as a function of the number of nodes.
The first blockchain of the Cosmos network is the Cosmos Hub, launched in 2019. It is a proof-of-stake blockchain with ATOM as its native token. Its role in the ecosystem is to work as the main hub via which application-specific blockchains can connect. It also provides bridges to Ethereum and Bitcoin. ATOM has a variable inflation rate and no hard cap on its maximum supply.
Business case
The total market capitalization of crypto assets has grown to over a trillion USD over recent years. However, the industry’s growth has been significantly hindered by scaling problems. Most blockchains and dapps can not efficiently process tens of thousands of transactions per second to serve millions of users across a diverse ecosystem of interconnected dapps. By providing vertical scalability (i.e., high transaction throughput on a single blockchain) and horizontal scalability (i.e., multi-chain architectures), Cosmos aims to solve arguably the most pressing issue in blockchain applications. Other projects, such as Polkadot with its parachains, are also starting to support interconnected application-specific blockchains.
The long-term development of the Cosmos ecosystem is supported by the Interchain Foundation (ICF), founded in 2016. The foundation is well funded and provides grants to teams working on expanding the Cosmos ecosystem. In 2017, ICF raised 16.8 million USD in ATOM’s initial coin offering (ICO). In 2021, the company raised further 21 million USD by selling ATOM in a round led by Paradigm.
Historical performance
Since its launch in 2019, the number of apps on the Cosmos network has grown to 263 as of April 2022. While most of these projects are small, some of them are well-funded and impactful blockchains, such as the Binance Smart Chain, Terra, and Crypto.com Chain. Since launch, 45 blockchains have been deployed on the Cosmos network.
This section provides a brief overview of the Cosmos Hub’s historical performance using Token Terminal’s data. For more information and to be able to interactively explore the shown data, make sure to check out our dashboard!
Let’s start by looking at the transaction fees which are a good indicator of the demand of a blockchain. Users of the Cosmos Hub pay transaction fees in ATOM. The protocol charges a fee of 2% and the rest is paid to the block validators. The figure below shows the total value of transaction fees paid since the beginning of 2021. We are not showing the fees prior to 2021 as they were significantly lower then.
Next, let’s look at project valuation using circulating market capitalization, i.e., the number of ATOM in circulation multiplied by its price, shown in the figure below. After 2 years of stagnant but volatile price development, the project’s valuation has grown by five to six fold over the past two years. The Cosmos Hub’s market cap reached 2 billion USD for the first time in the beginning of 2021 and has since reached over 12 billion USD during its peaks.
Ultimately, the value of the Cosmos ecosystem will depend on all blockchains in the network. Therefore, overall developer interest in Cosmos’ tools is crucial. In order to get a rough estimate of developer interest in the ecosystem, we can use the number of times Cosmos SDK has been starred (i.e., bookmarked) on GitHub, shown in the figure below. Developer interest started to grow significantly faster in March 2018 and seems to further have accelerated in February 2021.
Roadmap
The ICF maintains an official roadmap that contains a summary of the Cosmos ecosystem’s planned upgrades and improvements within one year. It mainly contains important technical improvements to the core components of the ecosystem (i.e., Cosmos Hub, Cosmos SDK, IBC, and Tendermint). These include things such as optimization of computations on the blockchain and liquid staking of ATOM to increase liquidity. Additionally, several improvements such as focus on supporting NFTs have been proposed but not placed on the official roadmap yet. ICF also supports over 40 projects with grants to grow the Cosmos ecosystem.
Conclusion
Cosmos’ goal is to build a multi-chain ecosystem where individual blockchains can be optimized to serve the needs of applications that scale to millions of users. The project is well-funded and in a good position to be a major player in the multi-chain future.
The authors of this content, or members, affiliates, or stakeholders of Token Terminal may be participating or are invested in protocols or tokens mentioned herein. The foregoing statement acts as a disclosure of potential conflicts of interest and is not a recommendation to purchase or invest in any token or participate in any protocol. Token Terminal does not recommend any particular course of action in relation to any token or protocol. The content herein is meant purely for educational and informational purposes only, and should not be relied upon as financial, investment, legal, tax or any other professional or other advice. None of the content and information herein is presented to induce or to attempt to induce any reader or other person to buy, sell or hold any token or participate in any protocol or enter into, or offer to enter into, any agreement for or with a view to buying or selling any token or participating in any protocol. Statements made herein (including statements of opinion, if any) are wholly generic and not tailored to take into account the personal needs and unique circumstances of any reader or any other person. Readers are strongly urged to exercise caution and have regard to their own personal needs and circumstances before making any decision to buy or sell any token or participate in any protocol. Observations and views expressed herein may be changed by Token Terminal at any time without notice. Token Terminal accepts no liability whatsoever for any losses or liabilities arising from the use of or reliance on any of this content.
Stay in the loop
Join our mailing list to get the latest insights!
Continue reading

Customer stories: Token Terminal’s Data Partnership with Linea
Through its partnership with Token Terminal, Linea turns transparency into a competitive advantage and continues to build trust with its growing community.
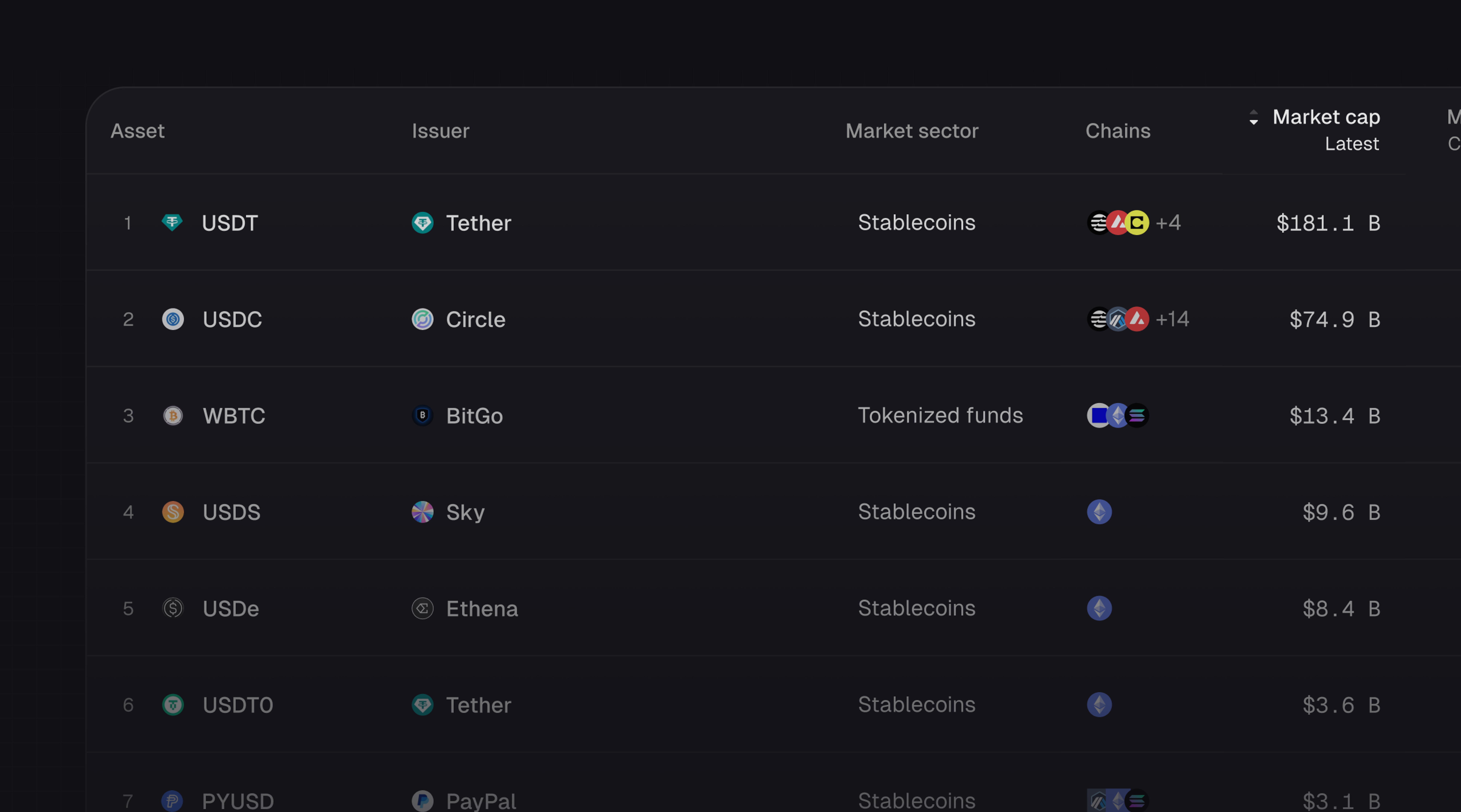
Introducing Tokenized Assets
Token Terminal is expanding its standardized onchain analytics to cover the rapidly growing category of tokenized real-world assets (RWAs) – starting with stablecoins, tokenized funds, and tokenized stocks.

Customer stories: Token Terminal’s Data Partnership with EigenCloud
Through its partnership with Token Terminal, EigenCloud turns transparency into a competitive advantage and continues to build trust with its growing community.